Special Note#
This article is Part 2 of the Gentoo Linux Installation Guide series: Desktop Configuration.
Series Navigation:
- Base Installation: Installing Gentoo base system from scratch
- Desktop Configuration (This Article): Graphics drivers, desktop environments, input methods, etc.
- Advanced Optimization: make.conf optimization, LTO, system maintenance
Previous Step: Base Installation
12. Post-Reboot Configuration#
Congratulations! You have completed the Gentoo base installation and successfully entered your new system (TTY interface).
The following sections are configured on demand. You can selectively configure and install based on your needs (server, desktop office, gaming, etc.).
Important: Check Profile and Update System
Before starting configuration, please confirm your Profile settings are correct again and ensure the system is up to date:
eselect profile list # List all available Profiles
eselect profile set <number> # Set selected Profile (e.g., desktop/plasma/systemd)
emerge -avuDN @world # Update system
Now let's configure the graphical interface and multimedia functions.
12.0 Network Check [Required]#
After logging in, please ensure your network connection is normal.
- Wired Network: Usually connects automatically.
- Wireless Network: Use
nmtui(NetworkManager) oriwctl(iwd) to connect to Wi-Fi.
12.1 Global Configuration (make.conf) [Required]#
Reference: make.conf · Handbook: VIDEO_CARDS · Advanced Section 13
/etc/portage/make.conf is Gentoo's global configuration file. At this stage, we only need to configure input devices and localization options.
Important Note
Basic make.conf settings were done in Base Installation Section 5.2. This section only adds desktop-related settings.
For details on compilation optimization, USE flags, license management etc., please check Advanced Section 13.
Configure make.conf#
vim /etc/portage/make.conf
Add or modify the following configurations:
# Input Devices
INPUT_DEVICES="libinput"
# Localization Settings
L10N="en en-US"
LINGUAS="en en_US"
# Desktop Environment Support
USE="${USE} wayland X pipewire pulseaudio alsa"
Configure Graphics Drivers (VIDEO_CARDS)#
Recommendation
According to Gentoo Handbook, it is recommended to use package.use instead of setting VIDEO_CARDS in make.conf for more flexible management.
Create package.use file and configure video cards:
mkdir -p /etc/portage/package.use
vim /etc/portage/package.use/video-cards
Choose settings based on your hardware (Reference table below):
# NVIDIA Graphics
# */* VIDEO_CARDS: nvidia
# AMD Graphics (Sea Islands and newer)
# */* VIDEO_CARDS: amdgpu radeonsi
# Intel Graphics
# */* VIDEO_CARDS: intel
# Virtual Machine (QEMU/KVM)
# */* VIDEO_CARDS: virgl
Graphics Hardware Reference Table (Click to expand)
| Platform | Discrete GPU | VIDEO_CARDS Value | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intel x86 | None | intel | See Intel Feature Support |
| x86/ARM | NVIDIA | nvidia | Proprietary (Recommended) |
| Any | NVIDIA (Except Maxwell/Pascal/Volta) | nouveau | Open Source (Poor Performance) |
| Any | AMD Sea Islands & newer | amdgpu radeonsi | Recommended (GCN 1.2+) |
| Any | ATI & older AMD | See Radeon Feature Support | Legacy |
| Any | Intel | intel | Integrated |
| Raspberry Pi | N/A | vc4 | VideoCore IV |
| QEMU/KVM | Any | virgl | Virtual GPU |
| WSL | Any | d3d12 | DirectX 12 |
Details:
12.2 Apply Configuration and Update System [Required]#
Apply new USE flags:
emerge --ask --newuse --deep @world
12.3 Graphics Drivers [Required]#
Reference: NVIDIA/nvidia-drivers
- NVIDIA Proprietary Driver:
emerge --ask x11-drivers/nvidia-drivers - AMD: Enable
VIDEO_CARDS: amdgpu radeonsiin/etc/portage/package.use/video-cards - Intel: Enable
VIDEO_CARDS: intelin/etc/portage/package.use/video-cards
Configure VAAPI Video Acceleration
Reference: VAAPI · nvidia-vaapi-driver
Globally Enable VAAPI: Add
vaapitoUSEin/etc/portage/make.conf.# Recompile affected packages emerge --ask --changed-use --deep @worldInstall Drivers and Tools:
emerge --ask media-video/libva-utils # Install vainfo for verificationSpecial Steps for NVIDIA Users:
emerge --ask media-libs/nvidia-vaapi-driver
Note
nvidia-vaapi-driver may have stability issues under Wayland (such as CUDA/OpenGL interop problems).
For details, refer to: NVIDIA Forums, Reddit, GitHub Issue.
NVIDIA users also need to enable DRM KMS in kernel parameters:
Edit /etc/default/grub, add nvidia_drm.modeset=1 to GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT.
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
Intel/AMD Users: Usually directly supported after installing graphics drivers.
- Verify:
Run
vainfoto check output. Success if no errors and supported Profiles are displayed.
About Firefox and Hardware Acceleration
- System
ffmpegmainly provides software decoding support for formats like H.264, AAC, HEVC, MP3. - Firefox (especially
firefox-bin) comes with its own FFmpeg library and will not automatically use system FFmpeg's NVDEC/NVENC for hardware decoding. - Please visit the
about:supportpage to check Firefox's actual hardware acceleration status.
NVIDIA Chromium Hardware Acceleration Configuration (Recommended Method) (No VAAPI needed, click to expand)
Tip
The following configuration applies to Chromium, Chrome, Edge, Electron applications (like VSCode).
Method 1: Use Flags Configuration File (Recommended)
This method doesn't require modifying .desktop files, and the browser can be correctly recognized as the default browser.
1. Environment Variables
Create ~/.config/environment.d/chromium-nvidia.conf:
# NVIDIA Environment Variables
__GLX_VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME=nvidia
__VK_LAYER_NV_optimus=NVIDIA_only
GBM_BACKEND=nvidia-drm
2. Chromium/Chrome Flags Configuration Create corresponding flags file:
- Chrome Stable:
~/.config/chrome-flags.conf - Chrome Unstable:
~/.config/chrome-dev-flags.conf - Chromium:
~/.config/chromium-flags.conf - Edge Beta:
~/.config/microsoft-edge-beta-flags.conf - Edge Dev:
~/.config/microsoft-edge-dev-flags.conf
Content as follows:
# Vulkan Video Acceleration Configuration
# NVIDIA + Wayland Hardware Acceleration Optimization
--enable-features=VulkanVideoDecoder,Vulkan,VulkanFromANGLE,DefaultANGLEVulkan
--ozone-platform=x11
--use-vulkan=native
--enable-zero-copy
--enable-gpu-rasterization
--ignore-gpu-blocklist
--enable-native-gpu-memory-buffers
3. Apply Configuration Re-login.
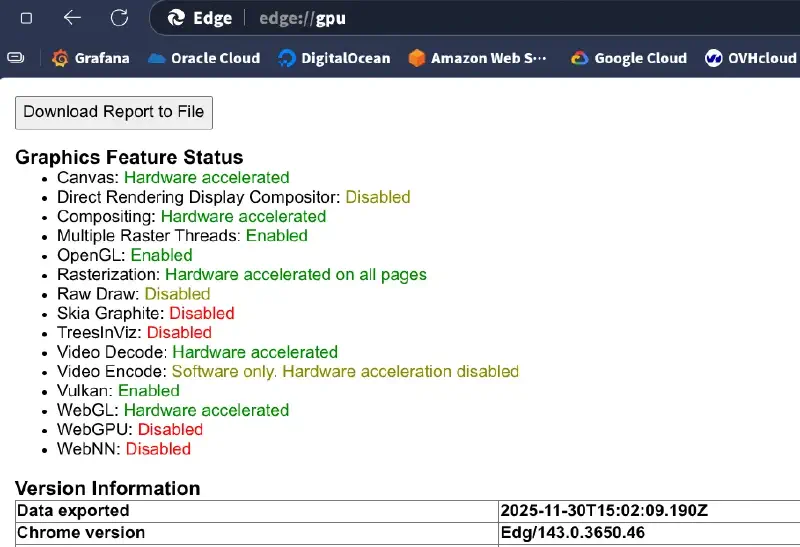
Verify: Visit
chrome://gpu/oredge://gpu/, check if Vulkan shows asEnabled.
12.4 Audio and Bluetooth [Optional]#
# Install PipeWire audio system and WirePlumber session manager
emerge --ask media-video/pipewire media-video/wireplumber
# Install Bluetooth stack, tools and manager (Blueman is GUI manager)
emerge --ask net-wireless/bluez net-wireless/bluez-tools net-wireless/blueman
Start Service (OpenRC)
rc-update add bluetooth default
/etc/init.d/bluetooth start
Start Service (Systemd)
# Enable Bluetooth service (system level):
sudo systemctl enable --now bluetooth
# Enable PipeWire core and PulseAudio compatibility layer
systemctl --user enable --now pipewire pipewire-pulse
# Enable WirePlumber session manager
systemctl --user enable --now wireplumber
12.5 Desktop Environments and Display Managers [Optional]#
KDE Plasma (Wayland)#
Reference: KDE
echo "kde-plasma/plasma-meta wayland" >> /etc/portage/package.use/plasma
emerge --ask kde-plasma/plasma-meta # Install Plasma Desktop
emerge --ask kde-apps/kde-apps-meta # (Optional) Install full KDE Apps suite
emerge --ask x11-misc/sddm # Install SDDM Display Manager
# OpenRC Configuration (SDDM has no independent init script)
# Reference: https://wiki.gentoo.org/wiki/Display_manager#OpenRC
emerge --ask gui-libs/display-manager-init # Install generic display manager init script
# Edit /etc/conf.d/display-manager
# Set DISPLAYMANAGER="sddm" and CHECKVT=7
sed -i 's/^DISPLAYMANAGER=.*/DISPLAYMANAGER="sddm"/' /etc/conf.d/display-manager
sed -i 's/^CHECKVT=.*/CHECKVT=7/' /etc/conf.d/display-manager
rc-update add display-manager default
rc-service display-manager start # Start immediately (Optional)
# Systemd Configuration
systemctl enable sddm
systemctl start sddm # Start immediately (Optional)
GNOME#
Reference: GNOME
emerge --ask gnome-base/gnome # Install GNOME core components
emerge --ask gnome-base/gdm # Install GDM Display Manager
rc-update add gdm default # OpenRC
systemctl enable gdm # Enable GDM Display Manager (systemd)
Hyprland (Wayland Dynamic Tiling Window Manager)#
Reference: Hyprland
emerge --ask gui-wm/hyprland
Tip
Hyprland requires newer graphics driver support. Recommended to read the Wiki for detailed configuration.
Other Options#
If you need a lightweight desktop, consider Xfce or LXQt:
- Xfce:
emerge --ask xfce-base/xfce4-meta(Wiki) - LXQt:
emerge --ask lxqt-base/lxqt-meta(Wiki) - Budgie:
emerge --ask gnome-extra/budgie-desktop(Wiki)
More Choices
For other desktop environments, please refer to Desktop environment.
12.6 Localization and Fonts [Optional]#
Reference: Localization/Guide · Fonts
To display Chinese properly, we need to install Chinese fonts.
# Install Noto CJK (Source Han) fonts
emerge --ask media-fonts/noto-cjk
# Install Emoji fonts
emerge --ask media-fonts/noto-emoji
# (Optional) WenQuanYi Micro Hei
emerge --ask media-fonts/wqy-microhei
Refresh font cache:
fc-cache -fv
12.7 Input Method Configuration (Fcitx5 & Rime) [Optional]#
Reference: Fcitx5
Rime is a powerful input method engine that supports multiple input schemes such as Hanyu Pinyin (Traditional/Simplified), Bopomofo, Terra Pinyin, etc.
For the best experience under Wayland, we need to configure environment variables.
Option A: Fcitx5 + Rime (KDE/General Recommendation)
Suitable for KDE Plasma, Hyprland and other environments.
Install Core Components
emerge --ask app-i18n/fcitx app-i18n/fcitx-configtoolInstall Language Engines Choose engines based on your language needs:
- Chinese (Rime):
emerge --ask app-i18n/fcitx-rime - Chinese (Pinyin):
emerge --ask app-i18n/fcitx-libpinyin - Japanese (Mozc):
emerge --ask app-i18n/fcitx-mozc - Korean (Hangul):
emerge --ask app-i18n/fcitx-hangul
- Chinese (Rime):
Configure Environment Variables (Wayland)
Reference: Using Fcitx 5 on Wayland
Edit /etc/environment:
vim /etc/environment
Write:
# Force XWayland apps to use Fcitx5
XMODIFIERS=@im=fcitx
# (Optional) For non-KDE environments or specific apps
GTK_IM_MODULE=fcitx
QT_IM_MODULE=fcitx
KDE User Tip
In KDE Plasma 5.27+, it's recommended to directly select Fcitx 5 in "System Settings" -> "Keyboard" -> "Virtual Keyboard" instead of manually setting the above environment variables (except XMODIFIERS).
- Start
- KDE/GNOME usually start automatically.
- Hyprland/Sway need to add
exec-once = fcitx5 -dto the configuration file.
Option B: IBus + Rime (GNOME Recommendation)
Reference: IBus
GNOME has the best integration with IBus, recommended priority.
Install Core Components
emerge --ask app-i18n/ibusInstall Language Engines Choose engines based on your language needs:
- Chinese (Rime):
emerge --ask app-i18n/ibus-rime - Japanese (Anthy):
emerge --ask app-i18n/ibus-anthy - Japanese (Mozc):
emerge --ask app-i18n/ibus-mozc - Korean (Hangul):
emerge --ask app-i18n/ibus-hangul
- Chinese (Rime):
Enable Go to GNOME Settings -> Keyboard -> Add Input Source -> Select "Chinese (Rime)" or your preferred language input method.
Rime Configuration Tips
- Switch Scheme: Press
F4key. - Supported Schemes: Hanyu Pinyin (Traditional/Simplified), Bopomofo, Terra Pinyin, etc.
- User Configuration Directory:
~/.local/share/fcitx5/rime(Fcitx5) or~/.config/ibus/rime(IBus).
12.8 Secure Boot [Optional]#
Reference: Secure Boot
If you need to enable Secure Boot, Gentoo recommends using sbctl to simplify configuration.
- Install sbctl:
emerge --ask app-crypt/sbctl - Enter BIOS Settings: Reboot into BIOS, set Secure Boot mode to "Setup Mode" (clear existing keys) and enable Secure Boot.
- Create and Enroll Keys:
Execute after entering the system:
sbctl create-keys sbctl enroll-keys -m # -m includes Microsoft keys (Recommended, otherwise may not boot Windows or load some firmware) - Sign Kernel and Bootloader:
# Automatically find and sign all known files (including kernel, systemd-boot, etc.) sbctl sign-all # Or manually sign (e.g., GRUB) # sbctl sign -s /efi/EFI/Gentoo/grubx64.efi - Verify:
sbctl verify
12.9 Portage Git Sync & Overlay [Optional]#
Why This Step?
Default rsync sync is slower. Using Git sync is not only faster but also easier to manage.
1. Install Git
emerge --ask dev-vcs/git
2. Configure Git Sync
mkdir -p /etc/portage/repos.conf
cp /usr/share/portage/config/repos.conf /etc/portage/repos.conf/gentoo.conf
Edit /etc/portage/repos.conf/gentoo.conf:
[DEFAULT]
main-repo = gentoo
[gentoo]
location = /var/db/repos/gentoo
sync-type = git
sync-uri = https://github.com/gentoo-mirror/gentoo.git
auto-sync = yes
Available Git mirror sources:
- GitHub (International):
https://github.com/gentoo-mirror/gentoo.git - BFSU (Beijing):
https://mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn/git/gentoo-portage.git - Tsinghua University:
https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/git/gentoo-portage.git
3. Add Gentoo-zh Overlay
Create a gentoo-zh.conf file in /etc/portage/repos.conf/ directory with the following content:
[gentoo-zh]
location = /var/db/repos/gentoo-zh
sync-type = git
sync-uri = https://github.com/microcai/gentoo-zh.git
auto-sync = yes
Available gentoo-zh Git mirror sources (Optional):
- Original Source (GitHub):
https://github.com/microcai/gentoo-zh.git - Chongqing University:
https://mirrors.cqu.edu.cn/git/gentoo-zh.git - Nanjing University:
https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/git/gentoo-zh.git
gentoo-zh distfiles mirror (Optional): To accelerate downloads of packages in the gentoo-zh overlay, you can use the following distfiles mirrors:
- Original Source:
https://distfiles.gentoocn.org/ - Chongqing University:
https://mirror.cqu.edu.cn/gentoo-zh - Nanjing University:
https://mirror.nju.edu.cn/gentoo-zh
Usage help: https://t.me/gentoocn/56
Important Update (Updated: 2025-10-07)
According to Gentoo's official announcement, Gentoo has stopped providing cache mirror support for third-party repositories. Starting from 2025-10-30, mirror configurations for all third-party repositories (including gentoo-zh) will be removed from the official repository list.
What does this mean?
- Tools like
eselect repositoryandlaymanstill work normally. - Officials will no longer provide cache mirrors, instead syncing directly from upstream sources (GitHub).
- Official repositories (
::gentoo,::guru,::kde,::science) are not affected and can still use mirrors.
If you have previously added the gentoo-zh overlay, please update the sync URI:
# Check installed repositories
eselect repository list -i
# Remove old configuration
eselect repository remove gentoo-zh
# Re-enable (will automatically use the correct upstream source)
eselect repository enable gentoo-zh
4. Execute Sync
emerge --sync
5. Software Installation Demo
For example, installing flclash-bin:
emerge -pv flclash-bin
Output example:
These are the packages that would be merged, in order:
Calculating dependencies
... done!
Dependency resolution took 0.45 s (backtrack: 0/20).
[ebuild N ] dev-libs/keybinder-0.3.2-r300:3::gentoo USE="introspection" 371 KiB
[ebuild N ] x11-apps/xmessage-1.0.7::gentoo 126 KiB
[ebuild N ] net-proxy/flclash-bin-0.8.90::gentoo-zh 39,565 KiB
Total: 3 packages (3 new), Size of downloads: 40,061 KiB
After confirming no errors, execute installation:
emerge --ask flclash-bin
12.10 Flatpak Support and Software Center [Optional]#
Reference: Flatpak
If you need to use Flatpak or want to manage Flatpak applications in the Software Center:
Install Flatpak
emerge --ask sys-apps/flatpakEnable Software Center Support To let GNOME Software or KDE Discover support Flatpak, enable the corresponding USE flag.
GNOME Users: Add to
/etc/portage/package.use/gnome(or create a new file):gnome-extra/gnome-software flatpakKDE Users: Add to
/etc/portage/package.use/kde(or create a new file):kde-plasma/discover flatpakUpdate Software Center
# GNOME emerge --ask --newuse gnome-extra/gnome-software # KDE emerge --ask --newuse kde-plasma/discover
Usage Tip
Flatpak is very suitable for installing proprietary software (like QQ, WeChat). Its sandbox isolation mechanism ensures main system security and cleanliness.
# Search applications
flatpak search qq
flatpak search wechat
# Install QQ and WeChat
flatpak install com.qq.QQ
flatpak install com.tencent.WeChat
12.11 System Maintenance (SSD TRIM & Power Management) [Optional]#
1. SSD TRIM (Extend SSD Life)
Reference: SSD
Regular TRIM execution can maintain SSD performance.
Check Support
Run lsblk --discard. If the DISC-GRAN column is non-zero, TRIM is supported.
- Systemd Users:
systemctl enable --now fstrim.timer - OpenRC Users:
Recommended to run
fstrim -avmanually every week, or configure a cron task.
2. Power Management (Recommended for Laptop Users)
Reference: Power management/Guide
Please choose one of the following options (do not install both):
Option A: TLP (Recommended, Extreme Power Saving) Automatically optimizes battery life, suitable for most users.
emerge --ask sys-power/tlp
# OpenRC
rc-update add tlp default
/etc/init.d/tlp start
# Systemd
systemctl enable --now tlp
Configuration Tip
TLP's default configuration is excellent enough. For fine-tuning, the configuration file is located at /etc/tlp.conf. Run tlp start to take effect after modification.
Option B: power-profiles-daemon (Desktop Integration) Suitable for GNOME/KDE users, can switch "Performance/Balanced/Power Saver" modes directly in the system menu.
emerge --ask sys-power/power-profiles-daemon
# OpenRC
rc-update add power-profiles-daemon default
/etc/init.d/power-profiles-daemon start
# Systemd
systemctl enable --now power-profiles-daemon
3. Zram (Memory Compression)
Recommended
Zram can create a compressed memory swap partition, effectively preventing Out of Memory (OOM) when compiling large software.
OpenRC Users:
emerge --ask sys-block/zram-init
rc-update add zram-init default
Configuration located at /etc/conf.d/zram-init
Systemd Users:
Recommended to use zram-generator:
emerge --ask sys-apps/zram-generator
# Create default configuration (Automatically use 50% memory as Swap)
echo '[zram0]' > /etc/systemd/zram-generator.conf
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start dev-zram0.swap
Next Step: Advanced Optimization









